Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) has become a significant topic in medical circles and among those who suffer from low testosterone levels. While there are various methods to administer TRT, two of the most debated forms are the cream and the injections. This article delves deep into these two methods, analyzing their benefits and drawbacks to provide a comprehensive perspective.
Key Points:
Comparison of TRT Methods: TRT creams are user-friendly and offer continuous hormone release, whereas injections are more direct but may require dealing with needles. Each method has distinct benefits and potential challenges, emphasizing the importance of individual suitability.
Study Findings: Studies show TRT cream effectively increases testosterone levels and improves sexual function, while injections have been studied for their long-term cardiovascular effects and effectiveness in specific conditions like chronic kidney disease.
Choosing the Right Method: The choice between cream and injections depends on individual factors like lifestyle, comfort with application methods, and frequency preferences. Consultation with healthcare professionals is essential for an informed decision.
TRT Cream
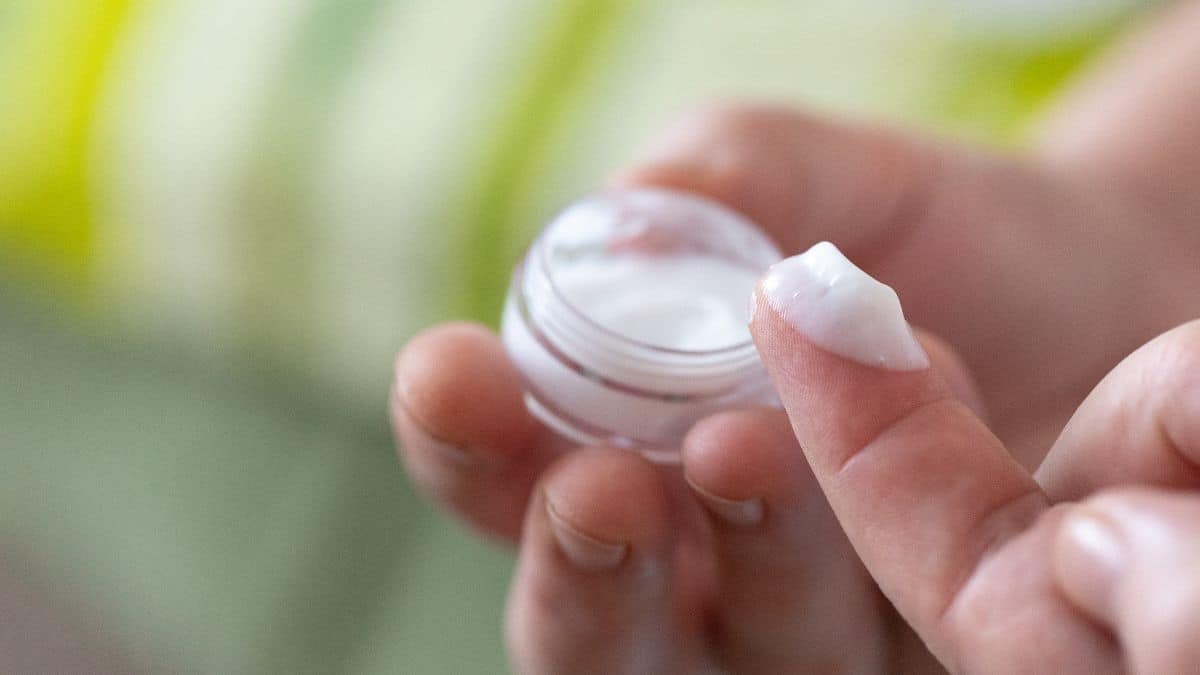

TRT cream is a topical application that contains synthesized testosterone. It's typically formulated with carriers that ensure optimal absorption through the skin. The precise ingredients might vary between brands, but the primary active component remains testosterone.
Once applied to the skin, the testosterone in the cream is gradually absorbed into the bloodstream. This process aims to mimic the body's natural rhythm of testosterone release, providing a steady level throughout the day.
Benefits of TRT Cream
Drawbacks of TRT Cream
Studies exploring the efficacy of TRT cream
Various studies have explored the effectiveness of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) cream in increasing testosterone levels:
Double-Blind Methodology Study:
A study employing a double-blind methodology found that 73% of the men using testosterone creams once daily saw a significant increase in their testosterone levels by the end of the study, as opposed to only 15% in the placebo group. This study also found improved sex drive and performance in the testosterone group, with no increased risk of heart attack or cardiovascular disease compared to the placebo group12.
Study on Sexual Function Improvement:
In a study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, it was found that TRT results in sexual function improvement when men with hypogonadism were considered, although it didn't specify the form of TRT used3.
90-day Treatment with Testosterone Gel:
A 90-day treatment of hypogonadal men with testosterone gel (a similar topical treatment to TRT cream) showed significant increases in osteoblastic activity markers and bone mineral density of the hip and spine in those receiving a 100 mg/day dose4.
Placebo-Controlled Trial by Marks et al.:
A study by Marks et al. observed an increase in serum testosterone and dihydrotestosterone levels in men on intramuscular TRT for 6 months, although it did not focus on topical TRT5.
TRT Injections
TRT injections usually contain testosterone cypionate, testosterone enanthate, or testosterone propionate suspended in oil. These formulations are designed for intramuscular injection, ensuring that the testosterone is slowly released into the bloodstream over time. These injections require a prescription in the US and widely available at clinics both online and offline.
Once injected into the muscle, the testosterone is gradually released into the bloodstream. Depending on the specific type and dosage of the injection, the intervals between shots can vary from weekly to every few weeks.
Benefits of TRT Injections
Drawbacks of TRT Injections
Studies exploring the efficacy of TRT injections
Comparative Study on Intramuscular Injection and Ointment:
A study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of a combined treatment involving intramuscular testosterone injection and testosterone ointment application with intramuscular injection monotherapy for late-onset hypogonadism (LOH)1.
TRAVERSE Study on Long-Term Effects:
The Testosterone Replacement therapy for Assessment of long-term Vascular Events and efficacy ResponSE in hypogonadal men (TRAVERSE) study is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group, non-inferiority, multicenter study which aimed to evaluate the long-term effects of testosterone treatment on cardiovascular health2.
Study on Chronic Kidney Disease Patients:
Another study investigated the safety and efficacy of TRT in men with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypogonadism. The efficacy of TRT was evaluated based on its influence on hormonal disorders, body composition, and erectile dysfunction3.
Investigation on Erectile Dysfunction:
A review of 73 articles was conducted to investigate the effects of testosterone replacement therapy on erectile dysfunction. This review included studies of intramuscular testosterone injections, among other TRT methods4.
General Efficacy in Hypogonadal Men:
A study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine outlined that TRT results in sexual function improvement when men with hypogonadism are considered. While it doesn't specify the form of TRT used, it's common for injections to be a method of administration in such studies5.
Key Differences between TRT Cream and Injections
Choosing the Right TRT Method
Importance of Individualized Treatment: No single TRT method suits everyone. Factors like age, lifestyle, medical history, and personal preferences play a significant role in the best choice.
Factors to Consider: Consider daily routine, comfort with injections, the desired frequency of administration, and potential side effects.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals: Before deciding on any TRT method, it's crucial to discuss options with a healthcare provider familiar with testosterone therapies.
Conclusion
TRT, whether through creams or injections, offers a lifeline to those grappling with the symptoms of low testosterone. While each method has its advantages and drawbacks, the key lies in understanding one's individual needs and consulting with medical professionals. Both approaches aim to improve the quality of life, and the right choice often hinges on personal preferences and specific circumstances.







